| Home | > | List of families | > | Ebenaceae | > | Diospyros | > | kirkii |
Diospyros kirkii
Selected images: Click on each image to see a larger version and details of the record View all images (11)
Detailed records: Display species records QDS maps by: Google Maps Point records by Google Maps
Species details: Click on each item to see an explanation of that item (Note: opens a new window)
| Synonyms: |
Diospyros baumii Gürke Diospyros latifolia Gürke Diospyros platyphylla Welw. ex Hiern |
| Common names: | Large-leaved jackal-berry (English) |
| Frequency: | |
| Status: | |
| Description: |
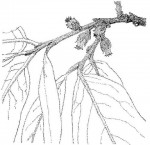
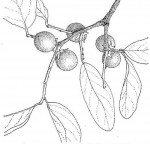
Small tree. Bark dark grey to blackish, very rough. Leaves spirally arranged, broadly elliptic to almost round, c. 8-18 cm long, dull green, hairy along the veins, particularly below; margin entire. Flowers in few-flowered axillary clusters, pinkish; covered in pinkish woolly hairs on the outside. Fruit fleshy, spherical, 3.5-4 cm in diameter, yellow to orange when ripe, tightly held in 4-5-lobed persistent calyx. The fruits are edible and much sought after. |
| Type location: |
Mozambique |
| Notes: | |
| Derivation of specific name: | kirkii: named after Dr John Kirk, who accompanied David Livingstone on his Zambezi expedition of 1858 |
| Habitat: | |
| Altitude range: (metres) | |
| Flowering time: | Sep - Nov |
| Worldwide distribution: | Angola, Shaba-DRC, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, Zimbabwe |
| National distribution: | |
| Growth form(s): | Tree. |
| Endemic status: | |
| Red data list status: | |
| Insects associated with this species: | |
| Spot characters: | Display spot characters for this species |
| Literature: |
Burrows, J.E., Burrows, S.M., Lötter, M.C. & Schmidt, E. (2018). Trees and Shrubs Mozambique Publishing Print Matters (Pty), Cape Town. Page 749. (Includes a picture). Drummond, R.B. (1975). A list of trees, shrubs and woody climbers indigenous or naturalised in Rhodesia. Kirkia 10(1) Page 266. Jacobsen, W.B.G. (1967). The influence of copper content of the soil on trees and shrubs of Molly South Hill, Mangula Kirkia 6(1) Pages 63 - 84. Mapaura, A. & Timberlake, J. (eds) (2004). A checklist of Zimbabwean vascular plants Southern African Botanical Diversity Network Report No. 33 Sabonet, Pretoria and Harare Page 39. Setshogo, M.P. (2005). Preliminary checklist of the plants of Botswana. Sabonet Report no. 37. Sabonet, Pretoria and Gaborone Page 54. Strugnell, A.M. (2006). A Checklist of the Spermatophytes of Mount Mulanje, Malawi Scripta Botanica Belgica 34 National Botanic Garden of Belgium Page 80. White, F. (1983). Ebenaceae Flora Zambesiaca 7(1) Pages 284 - 286. (Includes a picture). |
Other sources of information about Diospyros kirkii:
Our websites:
Flora of Malawi: Diospyros kirkiiFlora of Mozambique: Diospyros kirkii
Flora of Zambia: Diospyros kirkii
Flora of Zimbabwe: Diospyros kirkii
External websites:
African Plants: A Photo Guide (Senckenberg): Diospyros kirkiiAfrican Plant Database: Diospyros kirkii
BHL (Biodiversity Heritage Library): Diospyros kirkii
EOL (Encyclopedia of Life): Diospyros kirkii
GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility): Diospyros kirkii
Google: Web - Images - Scholar
iNaturalist: Diospyros kirkii
IPNI (International Plant Names Index): Diospyros kirkii
JSTOR Plant Science: Diospyros kirkii
Mansfeld World Database of Agricultural and Horticultural Crops: Diospyros kirkii
Plants of the World Online: Diospyros kirkii
Tropicos: Diospyros kirkii
Wikipedia: Diospyros kirkii
| Home | > | List of families | > | Ebenaceae | > | Diospyros | > | kirkii |